The entirety of LRN 12 and LRN 27 were assigned as part of US Route 80 upon the commissioning of the US Route System. The new system was formally designated by the American Association of State Highway Officials (AASHO) on November 11, 1926. The original description of US Route 80 in California can be seen below.
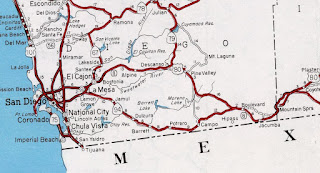
During 1934 the American Association of State Highway Officials (AASHO) approved a Division of Highways request to extend US Route 395 to San Diego. The city of San Diego map depicts US Route 80 and US Route 395 beginning concurrently at US Route 101 at the intersection of Market Street/12th Avenue. US Route 80/US Route 395 are shown following Park Avenue north out of downtown San Diego and east towards La Mesa via El Cajon Avenue (now El Cajon Boulevard).
US Route 395 is shown to depart US Route 80 via Fairmont Avenue on the San Diego County map. US Route 80 is depicted as following El Cajon Avenue east from San Diego to La Mesa. Within in La Mesa the routing is shown to dip down to what is now University Avenue and follow it through the city. The corridor is shown to follow a series of jogging roads east of La Mesa into El Cajon via what is now El Cajon Boulevard. US Route 80 is shown using Main Street through El Cajon and departing the city via what is now the Interstate 8 Business Route. From El Cajon the routing is of US Route 80 is shown using what is now Old Highway 80 and Alpine Boulevard to reach Alpine.
US Route 80 east from Alpine is shown using what is now Alpine Boulevard and Willows Road to the vicinity of Interstate 8 exit 36. US Route 80 is shown being carried by what is now Wildwood Glen Lane to Descanso Junction. US Route 80 is shown to be aligned over what is now California State Route 79 from Descanso Junction and branching onto what is now Old Highway 80 towards Pine Valley. From Pine Valley the alignment of US Route 80 is now Old Highway 80 to Manzanita. From Manzanita the alignment of US Route 80 followed modern California State Route 94 to another segment now signed as Old Highway 80 through Boulevard towards Jucumba. East of Jucumba, the alignment of US Route 80 meets the eastbound lanes of Interstate 8 descending into Imperial County via the Mountain Springs Grade.
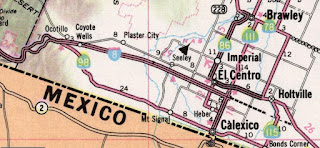
The Imperial County map depicts US Route 80 following mostly the eastbound lanes of Interstate 8 through the Mountain Springs Grade. Abandoned portions of the early highway can be found in Mountain Springs and In-Ko-Pah Gorge along Myers Creek. US Route 80 is shown to follow modern-day San Diego County Route S80 (Evan Hewes Highway) through Dixieland, Seeley, and El Centro and to California State Route 115 near Holtville. US Route 80 is depicted as following modern California State Route 115 through Holtville via 5th Street and Evan Hewes Highway towards Interstate 8. The alignment of US Route 80 is shown departing California State Route 115 and following as a northern frontage of Interstate 8 towards exit 151. East of All American Canal the alignment of US Route 80 is shown following Grays Well Road roughly to Interstate 8 exit 170. US Route 80 is shown to emerge from the grade of Interstate 8 onto Araz Station Road and towards Winterhaven. US Route 80 transitioned onto Winterhaven Drive and Quechan Road in Winterhaven towards the Colorado River via the Ocean-to-Ocean Bridge at the Arizona state line.
The
1938 Division of Highways Map displays US Route 80 ending in downtown San Diego via multiplex with US Route 395 on Park Boulevard at US Route 101/Broadway.
The
November 1938 California Highways & Public Works featured the opening of construction on the new alignment of the Mountain Springs Grade. The new alignment is cited to eliminate sixteen curves and almost one thousand degrees of curvature. Work is noted to have begun via a ceremony held on October 29, 1938.
Some commercial maps of the era such as the 1940 Gousha Highway Map hosted on usends.com
San Diego endpoint page depict US Route 80 ending at Point Loma. No published Division of Highways Map ever explicitly displayed US Route 80 ending at Point Loma.
The history of the Mountain Springs Grade is recapped within the article. The Mountain Springs Grade is noted to have originated as a Native American trail out of the Colorado River region of the Sonoran Desert. The early trail followed Carriso Creek through the In-Ko-Pah Mountains to what became Jacumba Hot Springs. This trail was explored by an expedition led by Juan Bautista de Anza during 1774. The routing through Carriso Gorge was in sporadic use through much of the Nineteenth Century.
Around 1870 (noted incorrectly as 1890) a new corridor through the In-Ko-Pah Mountains was plotted due to mining interests in Arizona. The new routing used In-Ko-Pah Gorge and would in time become known as the "Mountain Springs Grade." The Mountain Springs Grade was surveyed by San Diego County during 1908 and found to have a twenty-two percent grade. Corridor improvements began in 1912 first by San Diego County and Imperial County despite it being a First State Highway Bond Act corridor. The state assumed maintenance responsibilities beginning in 1914.
The
April 1941 California Highways & Public Works featured the start of construction along the final unit of the Mountain Springs Grade. The second and third units extended from the community of Mountain Springs east through In-Ko-Pah Gorge. Much of the planned corridor is shown to cutoff obsolete grades and would eliminate numerous curves. The second unit is noted to have begun work during July 1940.
The
May 1941 California Highways & Public Works announced plans for the Cabrillo Freeway through Balboa Park in San Diego. The article notes the corridor to primary serve as the new alignment of US Route 395 and does not overtly mention US Route 80. San Diego city voters approved a measure on March 25, 1941, to set aside a two hundred foot right of way for the Cabrillo Freeway to be constructed.
The
September 1941 California Highways & Public Works featured the then new cutoff alignment of US Route 80 between La Mesa and El Cajon. The improved corridor featured a new divided grade which served as an extension of El Cajon Boulevard. The new corridor bypassed the largely residential University Avenue in La Mesa.
The planned Cabrillo Freeway appears on the
1942 Division of Highways Map as part of LRN 77. The new cutoff between La Mesa and El Cajon can also be seen.
US Route 101 is depicted on the
1944 Division of Highways Map as being realigned through downtown San Diego via Harbor Drive. US Route 80 (multiplexed with US Route 395) is depicted as being extended through downtown San Diego via Market Street to US Route 101.
Camino Del Rio between US Route 395/LRN 77 and US Route 101/LRN 2 was taken under state maintenance as part of LRN 12 during 1953. This change appears on the
1954 Division of Highways Map. The addition of Camino Del Rio did not appear to have initially impacted the routing of US Route 80 in San Diego.
The
November/December 1954 California Highways & Public Works featured an article regarding the new crossing of the Colorado River along US Route 80 between Winterhaven and Yuma. The alignment adoption of the new bridge was selected by the California Highway Commission during May 1954.
The
1955 Division of Highways Map depicts the new US Route 80 bypass freeway of El Cajon and La Mesa connecting to US Route 101 via Camino Del Rio and the then newly acquired Alvarado Canyon Road. The map does not depict if US Route 80 was only realigned directly to US Route 101 or extended to Point Loma.
The
July/August 1955 California Highways & Public Works refers to Rosecrans Boulevard/LRN 12 between Lytton Street and Pacific Highway as part of US Route 80. This is the first known instance of US Route 80 being referenced as existing west of US Route 101.
The
November/December 1955 California Highways & Public Works announced the entirety of Federal Aid Second Route 732 was taken under state maintenance as a replacement for the outdated El Cajon Boulevard. The corridor is described as being annexed into LRN 12 and US Route 80. The design of the annexed routing along Alvarado Canyon Road and Camino Del Rio is described as being up to expressway standards. An extension of the Alvarado Canyon Road is described as being anticipated for completion towards El Cajon during July 1956.
The passage of the 1956 Federal Highway Aid Act brought the Interstate System into existence. The entirety of US Route 80 in California was assigned as a chargeable corridor which eligible for Federal Fund contribution matching. The major chargeable Interstate corridors can be seen on the August 1957 Interstate Highway System map. Interstate 8 can be seen following the general corridor of US Route 80.

The
March/April 1956 California Highways & Public Works featured the ongoing construction of the new Colorado River Bridge between Winterhaven and Yuma. The history of ferry service at Yuma is discussed in the article. The first ferry to provide service crossing the Colorado River began operations during 1850 and was later used by the Butterfield Overland Stage by 1858. The Southern Pacific Railroad would build a rail bridge in Yuma during 1878 but highway ferries would continue to operate until the completion of the Ocean-to-Ocean Bridge in 1915. The Southern Pacific Railroad would replace their original bridge with one next to the Ocean-to-Ocean Bridge in 1922.






A December 5, 1957, letter from the California State Highway Engineer to the AASHO Executive Secretary noted Arizona requested swapping the locations of Interstate 8 and 10. The California State Highway Engineer requested Interstate 12 be applied over established Intestate 10 and the latter number recycled over what was established Interstate 8. The same letter also requested Interstate 14 be applied to the future corridor of Interstate 210.
The January/February 1958 California Highways & Public Works describes the ongoing efforts to convert US Route 80 in San Diego to full freeway standards. The US Route 80/US Route 395 interchange is noted to be under schedule for construction later in the year. Another 1958 freeway conversion contract would span from US Route 395 east to the Fairmont Avenue.
A February 10, 1958, letter from the AASHO Executive Secretary to the California State Highway Engineer rejected the Interstate numbering schemes submitted during November and December 1957. The rejections are noted to have been due to the use of several low route numbers and not following the core conventions of Interstate route numberings.
The November/December 1958 California Highways & Public Works specifically stated US Route 80 ended at the Old Spanish Lighthouse at Point Loma. There is no instance of a documented request by the California Division of Highways to the AASHO to extend or realign US Route 80. It is likely such a request was not necessary given the movement of US Route 80 was entirely contained to San Diego and did not require a redefinition of the highway.
The same volume notes a public meeting was held at Jacumba to discuss the corridor alternatives for conversion of US Route 80 from Laguna Summit east to Coyote Wells via the Mountain Springs Grade to Interstate standards.
The then new channelized intersection of California State Route 98 and US Route 80 near Coyote Wells also appears in the same volume
1959 Legislative Chapter 1062 defined LRN 286 in the city of San Diego. The initial definition of the highway was "Sunset Cliffs Boulevard near Mission Bay southeasterly to LRN 2."
The
May/June 1959 California Highways & Public Works describes the upcoming freeway conversion of US Route 80 in Alvarado Canyon between Fairmont Avenue and Lake Murray Boulevard. The same article references another upcoming freeway conversion contract from Baltimore Drive to the recently completed section of US Route 80/Interstate 8 at Grossmont Summit. A future contract to extend the US Route 80/Interstate 8 freeway east to Magnolia Avenue (California State Route 67) in eastern El Cajon Valley is also discussed.
LRN 286 appears for the first time on the
1960 Division of Highways map. The corridor is shown to not have an alignment adoption but is projected as connecting US Route 101 (Interstate 5 and LRN 2) to Mission Bay roughly along Midway Drive.
The
May/June 1961 California Highways & Public Works describes the freeway corridor of US Route 80 as ending at US Route 101. The conversion of US Route 80 to Interstate standards in Mission Valley is noted to have been completed on December 23, 1960. The Mission Valley segment functionally made the initial ten miles of Interstate 8 east of US Route 101 fully functionally as a freeway. The conversion of US Route 80 to Interstate standards through El Cajon is noted to largely be anticipated for completion in segments during 1961 and 1962.
The
September/October 1961 California Highways & Public Works describes two completed freeway contracts on US Route 80/Interstate 8 through El Cajon. The freeway is described as being continuous west to US Route 101 sans a 2.3-milea segment through La Mesa due for completion during 1962.
The
November/December 1961 California Highways & Public Works notes money was allocated for the 1962-63 Fiscal Year for freeway construction along US Route 80 at the Mountain Springs Grade. The same article stub references a seven-mile segment of US Route 80/Interstate 8 being recently completed in the Algodones Dunes.
The
May/June 1963 California Highways & Public Works featured construction photos of US Route 80/Interstate 8 through Devil's Canyon on the Mountain Springs Grade. The westbound lanes of the new freeway were constructed through Devil's Canyon so the existing highway through In-Ko-Pah Gorge could be converted to eastbound-only traffic.
The
October/November 1963 California Highways & Public Works announced the adopted alignment of the LRN 286 freeway west of planned Interstate 5 in San Diego. The alignment was selected to run along the southern flank of the San Diego Flood Control Channel during the July/August 1963 California Highway Commission meetings.
As part of the 1964 State Highway Renumbering the Legislative Route Numbers were dropped. LRN 12 west of US Route 101 was assigned as part of
California State Route 209. The
1964 Division of Highways Map depicts California State Route 209 as ending at Point Loma but does not clearly convey the status of US Route 80 west of US Route 101. The LRN 286 freeway corridor was reassigned as
California State Route 109.
The
January/February 1964 California Highways & Public Works featured the completed freeway through the Mountain Springs Grade. The article touches on several aspects of the early history of the corridor. During 1870, San Diego County granted toll franchise rights to the San Diego & Fort Yuma Turnpike Company to build a road through the Mountain Springs Grade.
The
September/October 1965 California Highways & Public Works featured the completed segment of Interstate 8 in eastern El Cajon to Lake Jennings Road. The publication noted the rapidly increasing population of metropolitan San Diego and estimated Interstate 8 would be completed in California by 1972. A segment of the freeway towards Alpine is shown to be in the process of construction and was estimated to be complete by 1966.
The
1966 Division of Highways map was the first edition to feature numerous alignment adoptions for Interstate 8 east of El Cajon. A planned grade is shown to bypass much of existing US Route 80 from Descanso east to Pine Valley. Another similar bypass of Boulevard of Jacumba to the Mountain Springs Grade is displayed. Much of Interstate 8 east from Coyote Wells is shown to have a planned routing south of the major Imperial Valley communities.
The
November/December 1966 California Highways & Public Works announced funding for construction of the California State Route 209 freeway was earmarked for the 1967-1968 fiscal year. Similarly, much of the construction of Interstate 8 in Imperial Valley was also earmarked for the 1967-1968 fiscal year. Additionally, funding was allocated to construct a rest area at Midway Wells at the Algodones Dunes.
On November 27, 1966, the AASHO approved a request by the Division of Highways to truncate US Route 80 to the Arizona State Line. The rationale behind the truncation of US Route 80 was that it was almost completely multiplexed with Interstate 8 east of Interstate 5. The attached Division of Highways Map depicts US Route 80 terminating at Point Loma. Oddly whoever drew the map of US Route 80 had accidentally applied it over California State Route 94 east of San Diego. This is the only known instance of US Route 80 being referred to as ending at Point Loma contained in the AASHTO Database.
The California Highways & Public Works publication ended during 1967 prior to the completion of Interstate 8 in the state. The
1967 Division of Highways map reveals the segment of the freeway bypassing Boulevard and Jacumba had opened during the prior year.
The completed Ocean Beach Freeway (California State Route 109) was dedicated during
October 1969. The freeway can be seen spanning west from Interstate 5/Interstate 8 to Sunset Cliffs Boulevard on the
1970 Division of Highways map.
1972 Legislative Chapter 1216 transferred the entirety of California State Route 109 to Interstate 8. Modern Interstate 8 west of Interstate 5 still maintains the Post Miles intermitted from the California State Route 109.
Notably, the transfer of California State Route 109 was not made in concurrence with an application to the Federal Highway Administration or AASHO to extend Interstate 8. The modern Federal Highway Administration
route log displays Interstate 8 as 169.92 miles long in California whereas "Route 8" as defined by the California legislature is 172 miles.
Interstate 8 east of El Cajon to the Imperial County line was designated as the "Kumeyaay Highway" by way of Assembly Concurrent Resolution 57, Chapter 112, in 1997. The designation was extended west to Nimitz Boulevard in San Diego by way of Assembly Concurrent Resolution 156, Chapter 90, during June 2002.










































































































































































































Comments