Upon leaving the Royal Gorge Bridge I headed east on US Route 50 to Colorado State Route 115. I next took CO 115 north to US Route 24 in Colorado Springs. From Colorado Springs I stayed on US Route 24 west to the start of the Pikes Peak Highway. My next destination was on the 14,115 foot summit of Pikes Peak.
This entry serves as the 25th entry in the 2016 Summer Mountain Trip Series. Part 25 covered the history of the Royal Gorge Bridge and can be found below.
2016 Summer Mountain Trip Part 25; the Royal Gorge Bridge
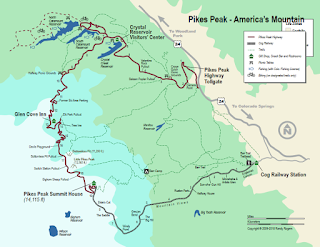
The Pikes Peak Highway is a 19.5 one-way ascent from US Route 24 to the 14,115 foot summit of Pikes Peak. The Pikes Peak Highway has 162 curves and has a sustained uphill grade of approximately 6.1%. The Pikes Peak Highway begins at an elevation of approximately 6,343 feet above sea level.
Much of the history of Pikes Peak can be found on the Pikes Peak Highway webpage. In 1803 the Front Range of the Rocky Mountains and Pikes Peak were added to American Territory as part of the Purchase. In 1806 numerous explorers were dispatched to survey the recently acquired lands of the Louisiana Purchase, Lt. Zebulon Montgomery Pike was charged with exploring the southern portion. The Pike expedition was the first American group to observe Pikes Peak. Pike along with several men made an attempt to summit Pikes Peak but apparently failed due to the cold November weather.
The first recorded ascent to the summit of Pikes Peak was in 1820 by Doctor Edwin James. Upon ascending the summit Dr. James named the mountain "James Peak." Despite Dr. James being the first to ascend Pikes Peak the Army Topographical Corps officially changed the mountain name to Pikes Peak in 1840. During the Colorado Gold Rush (originally called the Pikes Peak Gold Rush) of the 1850s and 1860s the summit of Pikes Peak became a land marker for settlers. Apparently the motto of the '59ers" (so called due to the Gold Rush beginning in 1859) was "Pikes Peak or bust!"
In 1888 the Cascade Town Company opened the Pikes Peak Carriage Road to traffic. The Pikes Peak Carriage Road would be quickly replaced in popularity when the Pikes Peak Cog Railway. The Pikes Peak Cog Railway began construction in 1889 and was completed to the summit of Pikes Peak in 1891. The Pikes Peak Cog Railway is 8.9 miles in length and is standard gauge line. By 1902 the Pikes Peak Carriage Road closed to traffic.
The current Pikes Peak Highway was financed by Spenser Penrose for $500,000 dollars and was completed by 1915. The Pikes Peak International Hillclimb (a time trail racing event) began the following year in 1916. The Pikes Peak Highway can be seen on the 1924 Rand McNally Regional Auto Trail Map.
The Pikes Peak Highway was maintained by the Colorado Department of Transportation between 1939 and 1947 as CO 250. The Pikes Peak Highway can be seen as CO 250 on the 1947 Shell Highway Map of Colorado.
For almost it's history the Pikes Peak Highway had a gravel surface. In 1998 through 1999 the Sierra Club pursued environmental litigation under the pretense that maintenance of Pikes Peak Highway was causing environmental damage due to gravel run-off. The City of Colorado Springs reached a settlement with the Sierra Club which led to the Pikes Peak Highway being completely paved by October 2011. The paving of the Pikes Peak Highway was a huge controversy in the racing world due to it changing the nature of the Pikes Peak International Hillclimb.
The Pikes Peak Highway is maintained nowadays by the City of Colorado Springs. Upon reaching the gates of the Pikes Peak Highways I was charged $5 dollars for being a single occupant in my rental car. Drivers are given instruction on how to ascend the mountain side (namely shutting off the air conditioner) and every vehicle gets a quick walk around inspection. Interestingly the Pikes Peak Highway is open all year even in the winter. During winter months drivers can reach heights where plowing becomes unfeasible. Speeds on the Pikes Peak Highway are highly enforced as a safety measure and are generally limited to 25 MPH.
From the tollgate the Pikes Peak Highway swings south to an overlook (Camera Point) of Hurricane Canyon. From the view point one can see US Route 24 and Manitou Springs below and to the southeast.
The Pikes Peak Highway swings northwest from Camera Point and passes by the Crystal Creek Reservoir. The Crystal Creek Reservoir is located at 9,230 feet above sea. The summit of Pikes Peak can be seen looking south from the Crystal Creek Reservoir.
The Pikes Peak Highway swings southwest from the Crystal Creek Reservoir past the starting point for the Pikes Peak International Hillclimb. The Pikes Peak Highway swings southward towards the Halfway Point Picnic Grounds and onward towards Glen Cove. Glen Cove is used as a brake check area from people returning from the top of Pikes Peak. During my descent from Pikes Peak I used second gear almost the entire time but it wasn't enough to keep my brakes cool. I was directed by the attendant at Glen Cove from telling me to park for 30 minutes. Fortunately Glen Cove has a deli which made it easy to pass the time.
From Glen Cove the Pikes Peak Highway climbs above the tree line and begins to curve through a series of massive switchbacks. These switchbacks are the most visually striking part of broadcasts of the Pikes Peak International Hillclimb. The photos below were taken near Devil's Playground.
I stopped at the Bottomless Pit View Point to have a look northward.
The switchback at the Bottomless Pit is easily to see given that the terrain is treeless.
Upon reaching the summit of Pikes Peak drivers are greeted with a sign announcing that they "made it" and the elevation of 14,115 feet above sea level.
The view from the summit of Pikes Peak looking northward.
A plaque dedicated to Lt. Zebulon Montgomery Pike can be found on the north face of Pikes Peak.
The Barr Trail and terminus of the Pikes Peak Cog Railroad can be found on the eastern flank of Pikes Peak.
The view from Pikes Peak looking west and southward.
Upon descending back to US Route 24 from the summit of Pikes Peak I turned west. My next destination was located at Florissant Fossil Beds National Monument.
2016 Summer Mountain Trip Part 27; Florissant Fossil Beds National Monument
This entry serves as the 25th entry in the 2016 Summer Mountain Trip Series. Part 25 covered the history of the Royal Gorge Bridge and can be found below.
2016 Summer Mountain Trip Part 25; the Royal Gorge Bridge
The Pikes Peak Highway is a 19.5 one-way ascent from US Route 24 to the 14,115 foot summit of Pikes Peak. The Pikes Peak Highway has 162 curves and has a sustained uphill grade of approximately 6.1%. The Pikes Peak Highway begins at an elevation of approximately 6,343 feet above sea level.
Much of the history of Pikes Peak can be found on the Pikes Peak Highway webpage. In 1803 the Front Range of the Rocky Mountains and Pikes Peak were added to American Territory as part of the Purchase. In 1806 numerous explorers were dispatched to survey the recently acquired lands of the Louisiana Purchase, Lt. Zebulon Montgomery Pike was charged with exploring the southern portion. The Pike expedition was the first American group to observe Pikes Peak. Pike along with several men made an attempt to summit Pikes Peak but apparently failed due to the cold November weather.
The first recorded ascent to the summit of Pikes Peak was in 1820 by Doctor Edwin James. Upon ascending the summit Dr. James named the mountain "James Peak." Despite Dr. James being the first to ascend Pikes Peak the Army Topographical Corps officially changed the mountain name to Pikes Peak in 1840. During the Colorado Gold Rush (originally called the Pikes Peak Gold Rush) of the 1850s and 1860s the summit of Pikes Peak became a land marker for settlers. Apparently the motto of the '59ers" (so called due to the Gold Rush beginning in 1859) was "Pikes Peak or bust!"
In 1888 the Cascade Town Company opened the Pikes Peak Carriage Road to traffic. The Pikes Peak Carriage Road would be quickly replaced in popularity when the Pikes Peak Cog Railway. The Pikes Peak Cog Railway began construction in 1889 and was completed to the summit of Pikes Peak in 1891. The Pikes Peak Cog Railway is 8.9 miles in length and is standard gauge line. By 1902 the Pikes Peak Carriage Road closed to traffic.
The current Pikes Peak Highway was financed by Spenser Penrose for $500,000 dollars and was completed by 1915. The Pikes Peak International Hillclimb (a time trail racing event) began the following year in 1916. The Pikes Peak Highway can be seen on the 1924 Rand McNally Regional Auto Trail Map.
The Pikes Peak Highway was maintained by the Colorado Department of Transportation between 1939 and 1947 as CO 250. The Pikes Peak Highway can be seen as CO 250 on the 1947 Shell Highway Map of Colorado.
For almost it's history the Pikes Peak Highway had a gravel surface. In 1998 through 1999 the Sierra Club pursued environmental litigation under the pretense that maintenance of Pikes Peak Highway was causing environmental damage due to gravel run-off. The City of Colorado Springs reached a settlement with the Sierra Club which led to the Pikes Peak Highway being completely paved by October 2011. The paving of the Pikes Peak Highway was a huge controversy in the racing world due to it changing the nature of the Pikes Peak International Hillclimb.
The Pikes Peak Highway is maintained nowadays by the City of Colorado Springs. Upon reaching the gates of the Pikes Peak Highways I was charged $5 dollars for being a single occupant in my rental car. Drivers are given instruction on how to ascend the mountain side (namely shutting off the air conditioner) and every vehicle gets a quick walk around inspection. Interestingly the Pikes Peak Highway is open all year even in the winter. During winter months drivers can reach heights where plowing becomes unfeasible. Speeds on the Pikes Peak Highway are highly enforced as a safety measure and are generally limited to 25 MPH.
From the tollgate the Pikes Peak Highway swings south to an overlook (Camera Point) of Hurricane Canyon. From the view point one can see US Route 24 and Manitou Springs below and to the southeast.
The Pikes Peak Highway swings northwest from Camera Point and passes by the Crystal Creek Reservoir. The Crystal Creek Reservoir is located at 9,230 feet above sea. The summit of Pikes Peak can be seen looking south from the Crystal Creek Reservoir.
The Pikes Peak Highway swings southwest from the Crystal Creek Reservoir past the starting point for the Pikes Peak International Hillclimb. The Pikes Peak Highway swings southward towards the Halfway Point Picnic Grounds and onward towards Glen Cove. Glen Cove is used as a brake check area from people returning from the top of Pikes Peak. During my descent from Pikes Peak I used second gear almost the entire time but it wasn't enough to keep my brakes cool. I was directed by the attendant at Glen Cove from telling me to park for 30 minutes. Fortunately Glen Cove has a deli which made it easy to pass the time.
From Glen Cove the Pikes Peak Highway climbs above the tree line and begins to curve through a series of massive switchbacks. These switchbacks are the most visually striking part of broadcasts of the Pikes Peak International Hillclimb. The photos below were taken near Devil's Playground.
I stopped at the Bottomless Pit View Point to have a look northward.
The switchback at the Bottomless Pit is easily to see given that the terrain is treeless.
Upon reaching the summit of Pikes Peak drivers are greeted with a sign announcing that they "made it" and the elevation of 14,115 feet above sea level.
The view from the summit of Pikes Peak looking northward.
A plaque dedicated to Lt. Zebulon Montgomery Pike can be found on the north face of Pikes Peak.
The Barr Trail and terminus of the Pikes Peak Cog Railroad can be found on the eastern flank of Pikes Peak.
The view from Pikes Peak looking west and southward.
Upon descending back to US Route 24 from the summit of Pikes Peak I turned west. My next destination was located at Florissant Fossil Beds National Monument.
2016 Summer Mountain Trip Part 27; Florissant Fossil Beds National Monument





























Comments